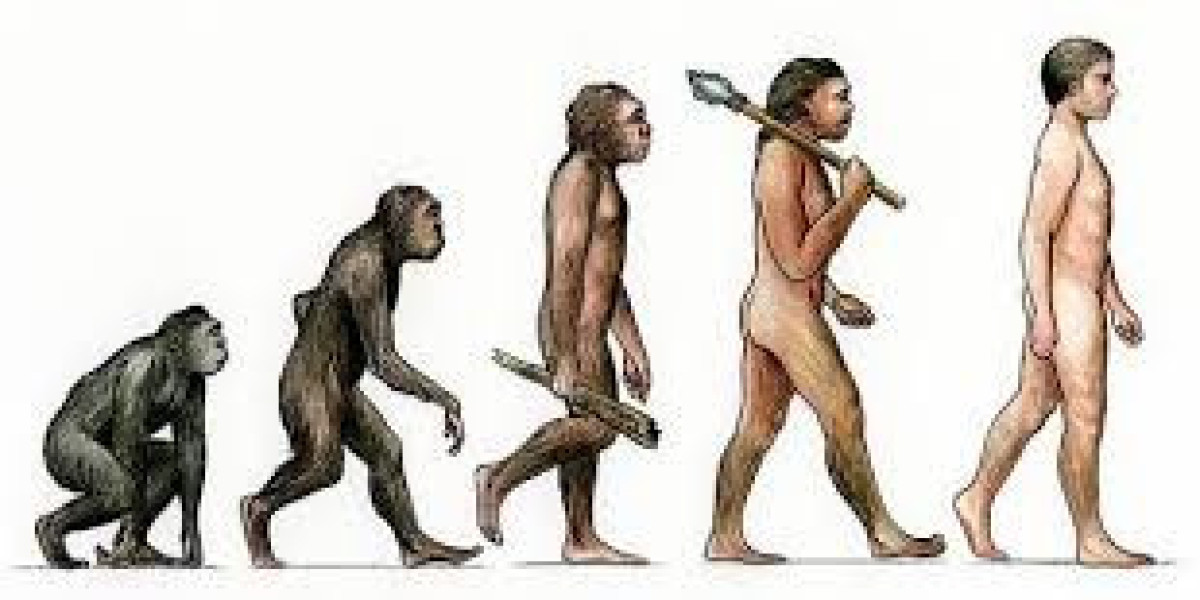
Human evolution, the process by which human beings developed on Earth from now-extinct primates. Viewed zoologically, we humans are Homo sapiens, a culture-bearing upright-walking species that lives on the ground and very likely first evolved in Africa about 315,000 years ago. We are now the only living members of what many zoologists refer to as the human tribe, Hominini, but there is abundant fossil evidence to indicate that we were preceded for millions of years by other hominins, such as Ardipithecus, Australopithecus, and other species of Homo, and that our species also lived for a time contemporaneously with at least one other member of our genus, H. neanderthalensis (the Neanderthals). In addition, we and our predecessors have always shared Earth with other apelike primates, from the modern-day gorilla to the long-extinct Dryopithecus. That we and the extinct hominins are somehow related and that we and the apes, both living and extinct, are also somehow related is accepted by anthropologists and biologists everywhere. Yet the exact nature of our evolutionary relationships has been the subject of debate and investigation since the great British naturalist Charles Darwin published his monumental books On the Origin of Species (1859) and The Descent of Man (1871). Darwin never claimed, as some of his Victorian contemporaries insisted he had, that “man was descended from the apes,” and modern scientists would view such a statement as a useless simplification—just as they would dismiss any popular notions that a certain extinct species is the “missing link” between humans and the apes. There is theoretically, however, a common ancestor that existed millions of years ago. This ancestral species does not constitute a “missing link” along a lineage but rather a node for divergence into separate lineages. This ancient primate has not been identified and may never be known with certainty, because fossil relationships are unclear even within the human lineage, which is more recent. In fact, the human “family tree” may be better described as a “family bush,” within which it is impossible to connect a full chronological series of species, leading to Homo sapiens, that experts can agree upon.
In biology, evolution is the change in the characteristics of a species over several generations and relies on the process of natural selection.
The theory of evolution is based on the idea that all species are related and gradually change over time.
Evolution relies on there being genetic variation in a population which affects the physical characteristics (phenotype) of an organism.
Some of these characteristics may give the individual an advantage over other individuals which they can then pass on to their offspring
Natural selection tells us more about how sir Charles darwin come up a theory.
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution states that evolution happens by natural selection.
Individuals in a species show variation in physical characteristics. This variation is because of differences in their genes.
Individuals with characteristics best suited to their environment are more likely to survive, finding food, avoiding predators and resisting disease. These individuals are more likely to reproduce and pass their genes on to their children.
Individuals that are poorly adapted to their environment are less likely to survive and reproduce. Therefore their genes are less likely to be passed on to the next generation.
As a consequence those individuals most suited to their environment survive and, given enough time, the species will gradually evolve.




Upendo Mandala 9 w
Nice